
Diabetes is a chronic health condition affecting millions of people worldwide, impacting how the body processes glucose (sugar) from the food we eat.
In this ultimate guide by e-Surgery, we’ll explore the intricacies of diabetes, from its definition and types to symptoms, diagnosis and management strategies.
Whether you’re newly diagnosed, caring for someone with diabetes, or simply seeking to understand this condition better, this ultimate guide will provide you with valuable insights and practical advice for navigating life with diabetes.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterised by consistently high blood glucose levels. This occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin or use it effectively. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels by allowing cells to absorb and use glucose for energy.
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body produces little or no insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can occur at any age.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form of diabetes, Type 2 occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. It’s often associated with lifestyle factors and typically develops in adults, though it’s increasingly seen in younger populations.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes lead to high blood sugar levels. While it usually resolves after childbirth, it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Understanding the type of diabetes you have is crucial for proper management and treatment. Each type requires a tailored approach to care, which we’ll explore further in this guide.
Symptoms & Risk Factors
It’s crucial to recognise the symptoms of diabetes for early diagnosis and treatment. While some people, especially those with prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes, may not experience noticeable symptoms initially, others may encounter them.
These can include increased thirst and frequent urination, unexplained weight loss (more common in Type 1), fatigue and weakness, blurred vision, slow-healing wounds or frequent infections, or tingling or numbness in hands or feet (in advanced stages).
It’s important to note that these symptoms can develop quickly in Type 1 diabetes, while they may appear gradually in Type 2 diabetes.
Although Type 1 diabetes is not preventable, there are several risk factors which increase the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. These include:
- Obesity or being overweight
- Family history of diabetes
- Age (risk increases after 45)
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Ethnicity (higher risk in certain populations, including South Asian, African, and African-Caribbean)
- History of gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- High blood pressure or high cholesterol
Diagnosis & Monitoring Diabetes
It’s essential that proper diagnosis and regular monitoring is carried out for effective diabetes management.
There are a few tests that healthcare providers use to diagnose the condition and assess blood glucose control. These are Fasting Plasma Glucose Test (measures blood sugar levels after an 8-hour fast), Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (checks how the body processes glucose over two hours after drinking a special sweet drink), and Glycated Haemoglobin Test (provides an average of blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months).
Once diagnosed, regular monitoring becomes crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Diabetes is usually monitored using a glucose meter to check blood sugar levels at home, HbA1c tests which are typically done every 3-6 months to assess long-term blood sugar control, and through regular check-ups.
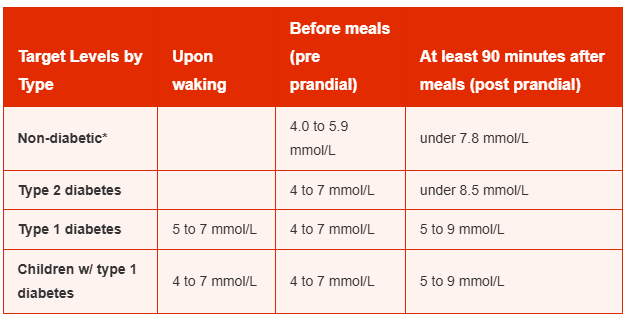
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes:
Treatment Options
Managing diabetes involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. The goal is to keep blood glucose levels within a target range to prevent complications and maintain overall health.
Medications
The type of medication prescribed depends on the type of diabetes and individual factors. For Type 1 diabetes insulin therapy is essential and life long as the body doesn’t produce insulin.
Patients that have Type 2 diabetes have medication options such as:
- Metformin: Usually the first-line medication, it improves insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: Stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
- DPP-4 inhibitors: Help the body continue to make insulin.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: Slow digestion and help lower blood glucose levels.
- SGLT2 inhibitors: Help the kidneys remove excess glucose through urine.
- Thiazolidinediones: Improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin.
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: Slow the digestion of carbohydrates.
e-Surgery offers two types of Type 2 Diabetes medication:
- Glucophage Tablets – from £14.95
- Metformin Tablets – from £7.95
Insulin Therapy
As mentioned, insulin therapy is crucial for Type 1 diabetes as the body doesn’t produce insulin, and it may also be necessary for some people with Type 2 diabetes. There are several types of insulin: rapid-acting insulin, short-acting insulin, intermediate-acting insulin, and long-acting insulin.
Lifestyle Medications
Alongside medication, lifestyle modifications play a vital role in diabetes management. These include:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on balanced meals, portion control, and carbohydrate counting.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Stress Reduction: Practice stress-management techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of diabetes complications.
These lifestyle changes not only help manage diabetes but also improve overall health and well-being.
Living With Diabetes
Successfully managing diabetes involves integrating care into your daily life. A key few aspects to consider include diet, exercise, and mental health.
Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. A few key dietary considerations include carbohydrate counting and choosing low glycaemic index foods, increasing fibre intake, limiting saturated fats and added sugars, practicing portion control, and staying hydrated.
Exercise
There are numerous benefits that physical activity has for people with diabetes, such as improving insulin sensitivity, help maintain a healthy weight, reducing cardiovascular risk, and aids in stress management.
You should aim for a mix of aerobic exercises and strength training. However, before starting a new exercise regimen consult with your healthcare provider.
Mental Health
It is possible that your mental health can be impacted when living with a chronic condition like diabetes. It’s important to address diabetes distress (where you feel overwhelmed by the demands of managing diabetes), depression and anxiety (which are more common in people with diabetes), and eating disorders (which can interfere with proper diabetes management).
Tips For Daily Management
It can be difficult to deal and manage diabetes on a day-to-day basis. Some tips that we suggest are:
- Create a routine for medication and monitoring
- Plan meals and snacks in advance
- Always carry fast-acting carbohydrates for low blood sugar episodes
- Wear medical ID
- Educate friends and family about your condition
- Join diabetes support groups for shared experienced and advice.
Next Steps
Living with diabetes requires ongoing attention and care, but with the right approach, it’s entirely possible to lead a healthy, fulfilling life. Remember these key points:
- Stay Informed: Continue to educate yourself about diabetes and stay up to date with the latest management techniques and research.
- Be Proactive: Take an active role in your care by monitoring your blood sugar, following your treatment plan, and making healthy lifestyle choices.
- Seek Support: Don’t hesitate to lean on family, friends, or support groups. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey.
- Plan For The Future: Consider long-term aspects of diabetes care, such as regular screenings for complications and adjusting your management plan as your needs change.
At e-Surgery, we’re committed to supporting you – from providing you with reliable information about the condition to offering quality medications, we’re help to help you navigate life with diabetes.
Additionally, whether you have questions about medication, need advice on lifestyle changes, or simply seek reassurance, you can use our ‘Ask-a-Pharmacist’ service where you can talk to a trained healthcare professional. We are always happy to help!










